It seems beyond doubt that accessible loan products such as microfinance have become one of the drivers of economic growth in local communities, especially in developing regions. This type of financing focuses heavily on small businesses, family farming, cultivation, or other self-employment environments that typically lack access to traditional loan products. Microfinance institutions (MFIs) became a necessary part to financial groups scaling in development markets. These institutions provide small loans for various purposes, enabling the ones in need to start new businesses, pursue education or other important community building initiatives. This boosts the local economy and improves the quality of life for people in the area.
Moreover, while the sum of loans is often trifling, the role of microfinance in the world economy is so influential that it cannot be ignored. Microfinance sector is growing rapidly, and various studies and predictions suggest that the market size will increase several times by 2030. Naturally, businesses within the industry have to scale as well. Increasing the number of clients and expanding one’s operations will allow keeping up with the growing demand and the changing needs of the borrowers.
Therefore, it is quite important that MFIs make every effort to anticipate the challenges associated with scaling. By doing so, they will be ready to implement strategic solutions that will permit effective and sustainable growth.
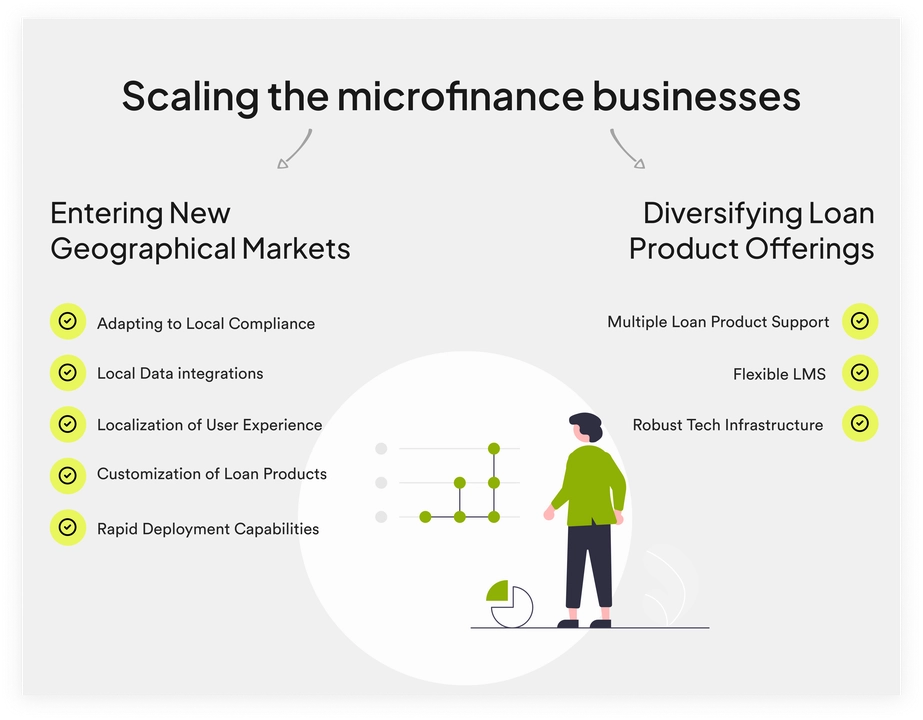
As microfinance institutions look towards expansion, there are two primary areas where the need to scale becomes apparent: entering new geographical markets and diversifying loan products. Both these domains require a robust strategy and technological support to navigate the complexities of scaling effectively.
Expanding into new geographical areas becomes an imperative to tap into untapped markets and broaden the base of beneficiaries. However, this expansion requires a robust technological framework capable of managing increased operational demands across diverse regions. Here are several factors that MFIs need to consider when scaling geographically:
Local Regulatory and Compliance Requirements: Each new geography comes with its own regulatory landscape, which can vary widely. MFIs must navigate varying compliance requirements, which can include everything from consumer protection laws to specific financial reporting standards. Understanding and integrating these local regulations into their operations is crucial to avoid legal pitfalls and maintain trust with local stakeholders.
Adaptation to Local Data Scenarios: In many developing regions, traditional credit data is scarce or non-existent. MFIs need to leverage alternative data sources such as utility bills, mobile phone usage, transactional underwriting, integrations into the merchant ecosystem, and social media footprints to assess creditworthiness. Open banking initiatives, where available, also provide a wealth of data that can help in crafting localized financial solutions.
Localization of User Experience: The success of financial products is often closely tied to how well they resonate with local users. Microfinance businesses need to understand local trends, preferences, and the digital literacy levels of various user cohorts. This will help them to adjust their interfaces and transaction processes to meet the expectations of the local population.
Customization of Loan Products: Products must be tailored to fit the economic and cultural context of each new market. This includes adjusting loan amounts, repayment structures, and interest rates to meet local needs.
Rapid Deployment Capabilities: To keep pace with market demands and competitive pressures, institutions must have the ability to quickly launch and scale new operations within these diverse markets.
The second area of scaling involves diversifying the types of loan products offered to address a broader spectrum of financial needs. As the reach of microfinance grows, so does the complexity of the financial products needed to serve newer audiences effectively. Here are the key considerations for MFIs:
Robust Technology Infrastructure: The backbone of any successful scaling operation in microfinance is a robust technology infrastructure. This includes an efficient loan origination system, a flexible scoring engine, an adaptable underwriting studio, and comprehensive servicing capabilities. Such a system should be easily configurable to reduce technical overhead, minimize risk, and adapt quickly based on user feedback and loan performance.
Flexible Loan Management Systems (LMS): A dynamic LMS allows microfinance institutions to adjust loan settings and workflows in response to real-time feedback and portfolio performance metrics. Flexibility in the LMS ensures that products remain relevant and effective over time, adapting to changes in market conditions and borrower behavior.
Innovative Product Building Tools: Institutions need advanced tools to A/B test different user strategies, assess underwriting models, and identify potentially pre-approved user cohorts. These tools help in fine-tuning products before full-scale launch, thereby optimizing performance and acceptance rates.
For microfinance businesses, scaling is a strategic endeavor that involves sophisticated planning and advanced technological support. Whether entering new markets or expanding product lines, the goal remains the same: to broaden financial inclusion and empower more underserved communities. By addressing these areas effectively, MFIs can not only enhance their impact but also ensure sustainable growth in an increasingly competitive landscape.
For MFIs poised for expansion, integrating advanced technological solutions is pivotal. Neofin offers a robust no-code SaaS platform that is designed to streamline and enhance the scalability of microfinance operations. The platform addresses various key operational aspects from underwriting and customer relationship management to compliance and past due control.
Neofin’s platform enables MFIs to create, test, and deploy financial products without the need for extensive coding knowledge. This democratizes the process of further product usage after set up, allowing non-technical staff to participate actively in product innovation and adaptation. By simplifying the creation and modification of financial products, institutions can respond more quickly to market changes and customer needs.
One of the critical aspects of scaling in microfinance is the ability to onboard new customers rapidly and in compliance with local regulations. Neofin provides an advanced digital onboarding solution with a proprietary Machine Learning-based 3D Liveness Detection, video verification, and data connectors to quickly integrate local KYC data providers in every market. This technology enables microfinance institutions to onboard customers quickly, reducing the entry barriers typically associated with expanding into new markets or launching new financial products.
Risk management is paramount in microfinance, especially when entering new markets with potentially higher risk profiles. Neofin's Underwriting Studio offers a workspace for underwriters and risk managers to build, test, and adjust scoring cards and risk policies. Most importantly, the studio's capabilities allow for the usage of alternative data such as transactional information gathered from the merchants, to bridge the data gaps that are frequently the case on the developing markets. Currently the studio has an extensive database of materials to build decision rules, including over 150 criteria types and more than 10,000 data attributes. Automation not only speeds up these processes but also helps reduce errors associated with manual handling.
Customer relationship management (CRM) and API integrations are essential for scaling operations. Neofin's CRM component is a lightweight solution that just includes a basic set of entities any microfinance product needs to keep the customer database well structured and accountable. API integrations part includes Neofin out-of-box integrations marketplace and data connectors that allow embedding any new data source in days time.
Managing loan repayments and maintaining contact with clients through various channels is streamlined with Neofin’s Past Due Control. This component enables communication through voice calls, SMS, and IVRs, enhancing customer service and repayment rates. Moreover, the Mobile API enables institutions to embed lending functionalities into their mobile apps, further enhancing the user experience by allowing customers to track their loan status conveniently from their mobile devices.
Neofin's platform is currently operational across three continents, evidencing its scalability and adaptability to diverse market conditions. Trusted by over 30 financial institutions and handling more than 100,000 daily loans, the platform's robustness is further supported by a team with over 100 years of combined experience in banking and fintech, all from an engineering team that hails from these sectors.
It is evident that for microfinance institutions, growth entails more than just increasing the number of clients – it also involves improving the quality and convenience of the services provided. Microfinance as a whole has already made impressive accomplishments in empowering underprivileged populations, particularly in developing countries, to take control of their finances. Nevertheless, it should not stop here because the environment is also changing, providing new challenges and opportunities.
Modern technologies such as Neofin’s microfinance software solution can be instrumental in transforming and simplifying businesses’ workflows, ensuring the microfinance institutions can adapt to their clients’ changing demands. This will be even more important since the businesses will enter new markets and start to offer new products. Thus, by emphasizing both technological development and strategic planning, microfinance businesses can succeed in expanding not just in size but also in positively impacting more people through enabling financial inclusion.